Objective
a way to improve the usability of spinal navigation user interfaces
Outcome
a tool-mounted display for surgical drill alignment
Publications
Can a Hand-Held Navigation Device Reduce Cognitive Load? A User-Centered Approach Evaluated by 18 Surgeons
C. Brendle*, L. Schütz*, J. Esteban*, S. Krieg, U. Eck, N. Navab, Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2020
* shared first author
Usability of Graphical Visualizations on a Tool-Mounted Interface for Spine Surgery
L. Schütz, C. Brendle, J. Esteban, S. Krieg, U. Eck, N. Navab, Journal of Imaging 7 (8), 159, Special Edition: “The Application of Imaging Technology in Medical Intervention and Surgery”, 2021
a way to improve the usability of spinal navigation user interfaces
Outcome
a tool-mounted display for surgical drill alignment
Publications
Can a Hand-Held Navigation Device Reduce Cognitive Load? A User-Centered Approach Evaluated by 18 Surgeons
C. Brendle*, L. Schütz*, J. Esteban*, S. Krieg, U. Eck, N. Navab, Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2020
* shared first author
Usability of Graphical Visualizations on a Tool-Mounted Interface for Spine Surgery
L. Schütz, C. Brendle, J. Esteban, S. Krieg, U. Eck, N. Navab, Journal of Imaging 7 (8), 159, Special Edition: “The Application of Imaging Technology in Medical Intervention and Surgery”, 2021
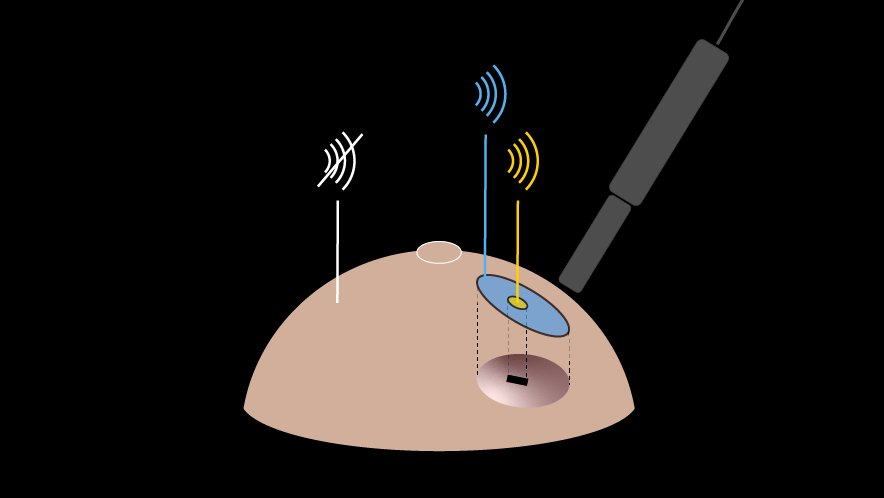
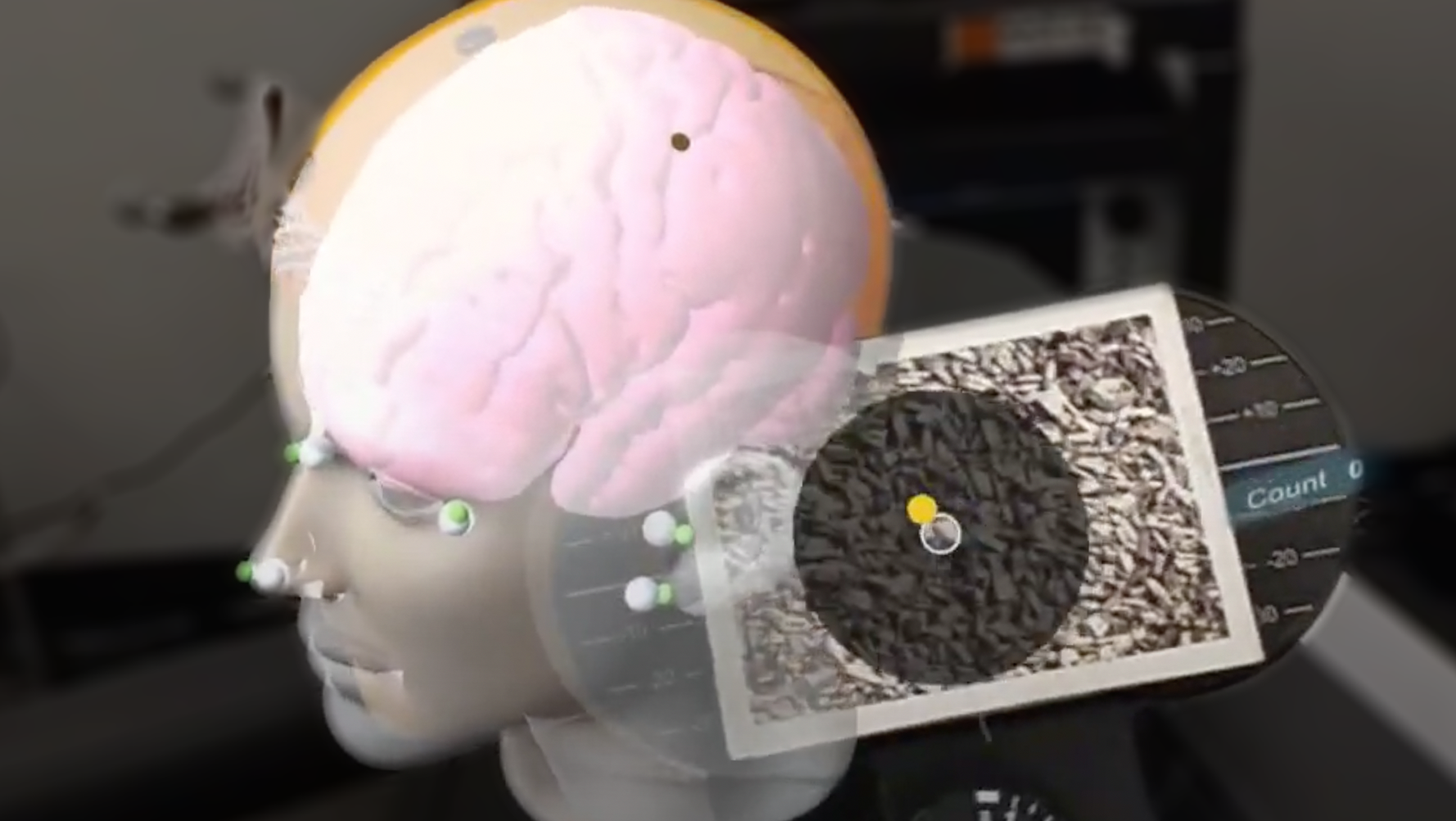
During spinal fusion surgery, the orientation of the pedicle screw in the right angle plays a crucial role for the outcome of the operation. Local separation of navigation information and the surgical situs, in combination with intricate visualizations, can limit the benefits of surgical navigation systems. The present study addresses these problems by proposing a hand-held navigation device (HND) for pedicle screw placement. The in-situ visualization and the simple integration of the device into the surgical workflow, allow the surgeon to position the tool while keeping sight of the anatomical target. 18 surgeons participated in a study comparing the HND to the state-of-the-art visualization on a desktop display. Our approach revealed significant improvements in mental demand and overall cognitive load, measured using a raw NASA-TLX (p < 0.05). Moreover, task time (p < 0.001) and system usability (p < 0.05) were significantly improved.
We present a user-centered navigation system for spinal fusion surgery. The solution consists of a hand-held navigation device (HND) which comprises a display for navigation information and a shaft for surgical tool guidance (Figure 1). This way, the HND enables the display of meaningful information in the surgeon’s field of view. The primary focus of this study is the evaluation of the HND for the task of angle alignment within the pedicle screw placement procedure.
Two different visualizations for angle orientation of the surgical tool were tested with 18 physicians against the visualizations used in clinical routine. The proposed visualizations were also tested against the same visualizations implemented on an external screen.
Our results show that this integration of the visualization unit into the HND, combined with a user-friendly visualization, reduces cognitive load when compared to the traditional approach. Furthermore, statistical analysis of the data showed that the proposed system presents a more time-efficient alternative to the state-of-the-art solutions.
Tools
Android Studio - Android App Development
Ticwatch E - Smart Watch
ImFusion - Desktop-based navigation UI & Tracking processing
NDI Polaris Vicra - Optical Tracking System
3D printing
Android Studio - Android App Development
Ticwatch E - Smart Watch
ImFusion - Desktop-based navigation UI & Tracking processing
NDI Polaris Vicra - Optical Tracking System
3D printing